
A LOOK INTO SUSTAINABILITY
WRITTEN BY HONOURABLE AYARUJA
"Sustainability," we're sure we've heard the term or heard someone mention it, especially in light of the global climate issue. So, what does sustainability entail, and how important is it? That is what we will concentrate on in this article.
The concept of sustainability first appeared in the Brundtland Report, published in 1987. This document which was also referred to as “Our Common Future”, was elaborated for the United Nations in order to warn about the negative environmental consequences of economic development and globalization It was written with the aim of offering solutions to the problems arising from industrialization and population growth.
DEFINITION
As a result, sustainability means meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. With the rise in environmental and social problems that societies around the world are facing, the term "sustainability" has come to mean "the processes and actions by which humankind avoids the depletion of natural resources in order to maintain an ecological balance that does not allow modern societies' quality of life to decline"
THE THREE PILLARS (UNDERSTANDING SUSTAINABILITY)
The idea is often broken down into three pillars: economic, environmental, and social sustainability—these principles are also informally used as profit, people, and planet.
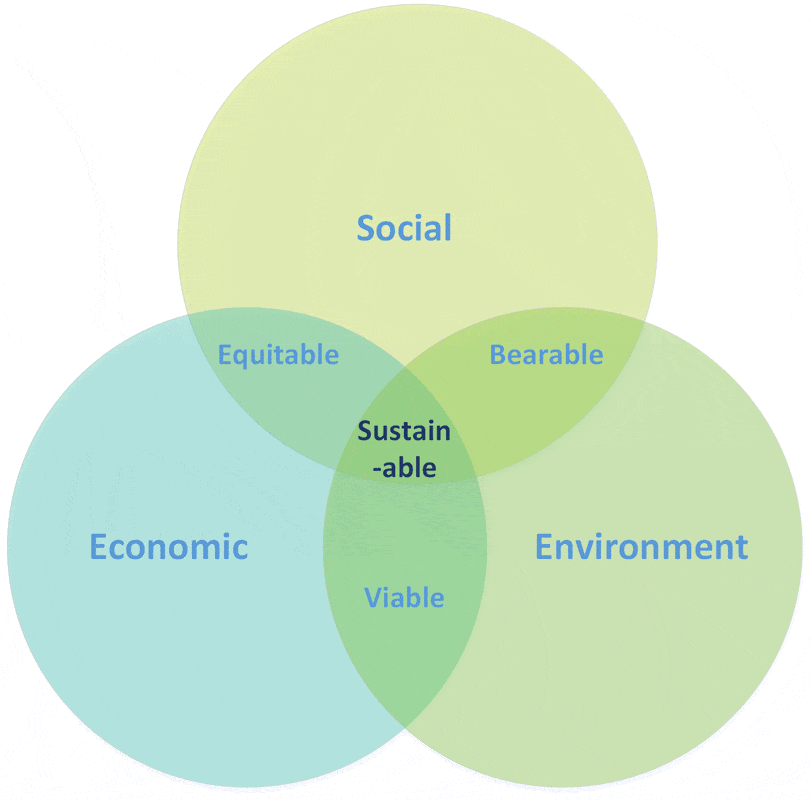
Economic Sustainability development (EcoSus):
This refers to strategies that promote long-term economic growth while minimizing negative effects on the community's social, environmental, and cultural components. It also refers to the efficient use of assets to maintain company profitability over time. As stated by the UK Government (Annual Report 2000, January 2001).
Here Human communities all over the world are able to keep their independence and have access to the resources they require to meet their needs, both financial and non-financial. Economic systems remain intact, and activities such as secure sources of livelihood are available to everyone. The difficulty with this type of sustainability is finding a balance. Rather than producing money at any cost, businesses should try to make money in a way that is consistent with other aspects of sustainability.
Environmental Sustainability development (EnvSus):
This is the most frequently discussed element, This is the management of our physical environment in a way that promotes living within ecological boundaries, protecting natural resources, and meeting community need without jeopardizing future generations' ability to meet their own needs. This would be accomplished by interacting with the environment responsibly in order to avoid depletion or deterioration of natural resources and to ensure long-term environmental quality.
As part of a supply chain, it is concerned with reducing carbon footprints, water usage, non-decomposable packaging, and wasteful operations. These methods are frequently both cost-effective and financially beneficial, as well as crucial for environmental sustainability.
Social Sustainability development (SocSus):
This is defined as a measure of human welfare. SocSus is not a concern regarding simple existence, but a wish to flourish and have the best lifestyle for which could dream (Abdel-Mohsen O. Mohamed, Evan K. Paleologos, in Pollution Assessment for Sustainable Practices in Applied Sciences and Engineering, 2021). Social sustainability is an often overlooked aspect of sustainability, as sustainable development discussions often focus on the environmental or economic aspects of sustainability
Its goal is to sustain social capital by investing in and developing services that make up our society's framework. The notion allows for a broader perspective of the world in terms of communities, cultures, and globalization. It entails safeguarding future generations and acknowledging that our actions have an influence on others and the planet at large. With principles like cohesiveness, reciprocity, and honesty, as well as the importance of interpersonal interactions, social sustainability focuses on maintaining and increasing social quality. It benefits people since living sustainably as individuals, families, communities, and countries means breathing cleaner air and spending less money on unnecessary healthcare.
BENEFITS OF SUSTAINABILITY (WHY IS SUSTAINABILITY IMPORTANT?)
There are both short- and long-term advantages to sustainability. If we do not make more sustainable decisions, we will not be able to maintain our Earth's ecosystems or continue to function as we do now. The concept of sustainability is based on the premise that individuals should not destroy the environment for the sake of short-term gain. It is required for life to exist. It has gotten a lot of attention as the effects of anthropogenic climate change have become more pervasive in modern life, ranging from uncomfortable heat waves to expensive and lethal weather catastrophes.
Some of the benefits include:
• Sustainability ensures the environment's health and biocapacity.
• Individual and community well-being are aided by sustainability.
• Sustainability encourages a more sustainable economy with less waste and pollution, fewer emissions, more jobs, and more equitable distribution of income.
Furthermore, sustainability tends to promote healthier lifestyles, such as favoring walking or cycling over driving. It advocates the consumption of fresh, locally produced foods over-processed foods. Warm, dry houses, which are conducive to health, are promoted by sustainability. It encourages people to choose natural goods instead of synthetic ones since they are safer.
Basically, By providing healthier living circumstances and better healthcare, sustainability can help to extend life expectancy and narrow the gap between affluent and poor people. Sustainable development promotes more responsible manufacturing and production, including waste and pollution from industry. It also pushes businesses, industries, and governments to make decisions based on the long-term implications rather than the simplest, cheapest solution.
